How do enzymes catalyze biological reactions select all that apply – How do enzymes catalyze biological reactions? This question lies at the heart of understanding the intricate dance of life’s molecular machinery. Enzymes, the master catalysts of biochemistry, orchestrate a symphony of chemical transformations that sustain all living organisms. This exploration delves into the mechanisms by which enzymes lower activation energies, facilitate substrate binding, and influence reaction rates, unveiling their pivotal role in biological processes.
How Enzymes Catalyze Biological Reactions
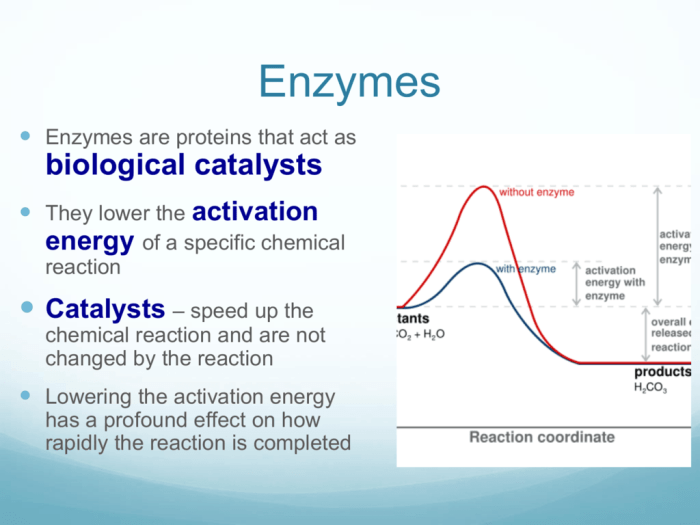
Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate the rate of chemical reactions in living organisms. They play a crucial role in various metabolic pathways, enabling the efficient functioning of cells and tissues.
Explain how enzymes lower the activation energy of biological reactions.
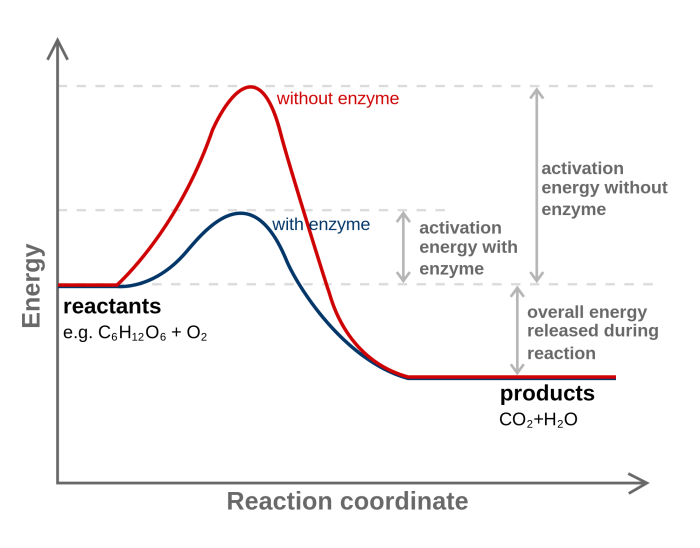
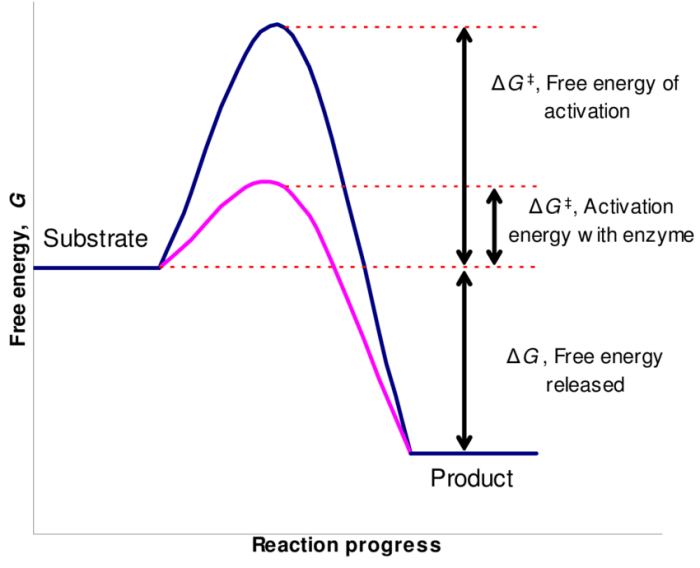
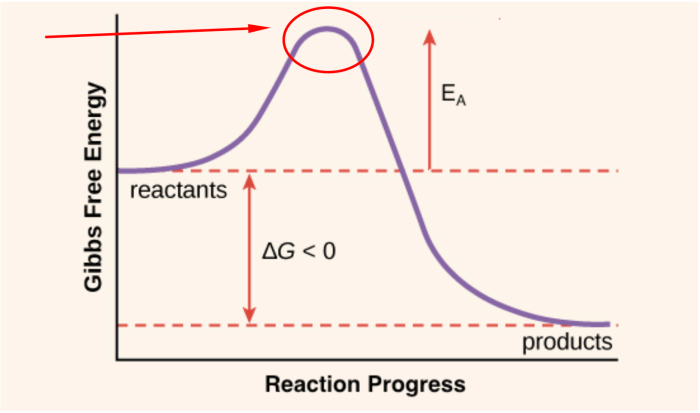
Enzymes reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to occur by providing an alternative pathway with a lower energy barrier. This alternative pathway involves the formation of an enzyme-substrate complex, which stabilizes the transition state of the reaction. The transition state is the high-energy intermediate that must be formed for the reaction to proceed.
By lowering the activation energy, enzymes make it easier for the reaction to take place, thereby increasing the reaction rate.
Describe the role of enzyme active sites in substrate binding.
Enzyme active sites are specific regions of the enzyme that bind to the substrate molecules. These active sites are highly complementary to the substrate, forming a lock-and-key fit. The active site provides a favorable environment for the reaction to occur by bringing the substrate molecules into close proximity and orienting them correctly.
The active site also contains specific amino acid residues that interact with the substrate, facilitating the chemical transformation.
Discuss the effects of enzyme concentration and temperature on reaction rates., How do enzymes catalyze biological reactions select all that apply
The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is influenced by the concentration of the enzyme and the temperature. Increasing the enzyme concentration leads to a higher probability of enzyme-substrate encounters, resulting in a faster reaction rate. However, at very high enzyme concentrations, the reaction rate may reach a plateau due to the saturation of the active sites.
Temperature also affects the reaction rate. Enzymes have an optimal temperature range at which they exhibit maximum activity. At temperatures below or above the optimum, the enzyme activity decreases. Extreme temperatures can cause denaturation of the enzyme, leading to a loss of its catalytic function.
Identify the types of enzyme inhibitors and explain their mechanisms of action.
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and reduce their catalytic activity. There are two main types of enzyme inhibitors: competitive inhibitors and non-competitive inhibitors.
- Competitive inhibitorsbind to the active site of the enzyme, competing with the substrate for binding. This competition reduces the number of enzyme-substrate complexes formed, thereby decreasing the reaction rate.
- Non-competitive inhibitorsbind to a different site on the enzyme, away from the active site. This binding causes a conformational change in the enzyme, altering the shape of the active site and reducing its affinity for the substrate. Non-competitive inhibitors do not compete with the substrate for binding, but they still reduce the enzyme’s catalytic activity.
Provide examples of how enzymes are used in biotechnology and medical applications.
Enzymes are widely used in biotechnology and medical applications. Some examples include:
- Industrial enzymes: Enzymes are used in various industrial processes, such as the production of biofuels, detergents, and food additives.
- Diagnostic enzymes: Enzymes are used in diagnostic tests to detect and measure the levels of specific substances in the body, such as glucose in blood or hormones in urine.
- Therapeutic enzymes: Enzymes are used as therapeutic agents to treat various diseases, such as enzyme replacement therapy for genetic disorders or thrombolytic enzymes to dissolve blood clots.
Commonly Asked Questions: How Do Enzymes Catalyze Biological Reactions Select All That Apply
What is the primary function of enzymes?
Enzymes serve as catalysts, accelerating the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process.
How do enzymes achieve their catalytic power?
Enzymes lower the activation energy required for reactions to occur, facilitating their progression.
What is the significance of enzyme active sites?
Active sites are specialized regions within enzymes that bind to specific substrates, enabling the catalytic process.
How do enzyme inhibitors impact enzyme activity?
Enzyme inhibitors bind to enzymes, either competitively or non-competitively, interfering with their ability to catalyze reactions.