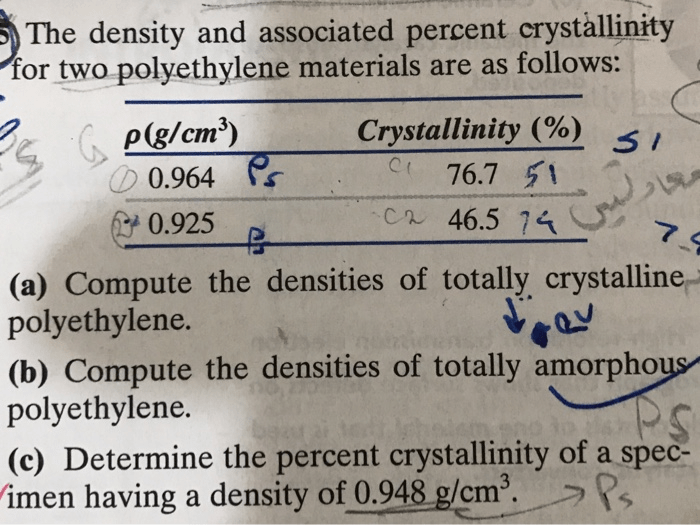The density and associated percent crystallinity are fundamental properties that provide insights into the structure and behavior of materials. Understanding these properties is crucial in diverse fields, ranging from materials science to engineering. This comprehensive exploration delves into the concepts, measurement techniques, influencing factors, and applications of density and percent crystallinity analysis, empowering readers with a profound understanding of these essential material characteristics.
Delving into the intricacies of density and percent crystallinity, this discourse elucidates their significance in characterizing materials. It unravels the methods employed to measure these properties, encompassing pycnometry, gas pycnometry, Archimedes’ principle, X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance.
Furthermore, it illuminates the factors that modulate density and percent crystallinity, including atomic packing, molecular weight, porosity, cooling rate, temperature, and the presence of impurities.
Understanding Density and Percent Crystallinity
Density, a fundamental property of materials, refers to the mass per unit volume. It provides insights into the atomic packing and molecular structure of materials. Percent crystallinity, on the other hand, quantifies the proportion of crystalline material within a sample.
Understanding these properties is crucial for characterizing materials and predicting their behavior in various applications.
Methods for Measuring Density and Percent Crystallinity
Density can be measured using techniques like pycnometry, gas pycnometry, and Archimedes’ principle. Pycnometry involves immersing a sample in a liquid of known density and measuring the displaced volume. Gas pycnometry utilizes the principle of gas displacement to determine volume.
Archimedes’ principle utilizes buoyancy to calculate density by measuring the weight difference of a sample in air and a fluid.
Percent crystallinity can be determined through methods such as X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. X-ray diffraction analyzes the diffraction patterns of X-rays passing through a sample, revealing the crystalline structure and percent crystallinity. Differential scanning calorimetry measures the heat flow during a temperature change, providing information about the melting behavior and percent crystallinity.
Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance uses the magnetic properties of nuclei to probe the molecular structure and crystallinity of materials.
Factors Affecting Density and Percent Crystallinity
Density is influenced by factors such as atomic packing, molecular weight, and porosity. Closely packed atoms and high molecular weight contribute to higher density. Porosity, on the other hand, reduces density. Percent crystallinity is affected by factors like cooling rate, temperature, and the presence of impurities.
Rapid cooling promotes the formation of amorphous or less crystalline structures, while slower cooling allows for the development of larger and more perfect crystals. Temperature influences the mobility of atoms and their ability to form ordered crystalline structures. Impurities can interfere with crystal growth and reduce percent crystallinity.
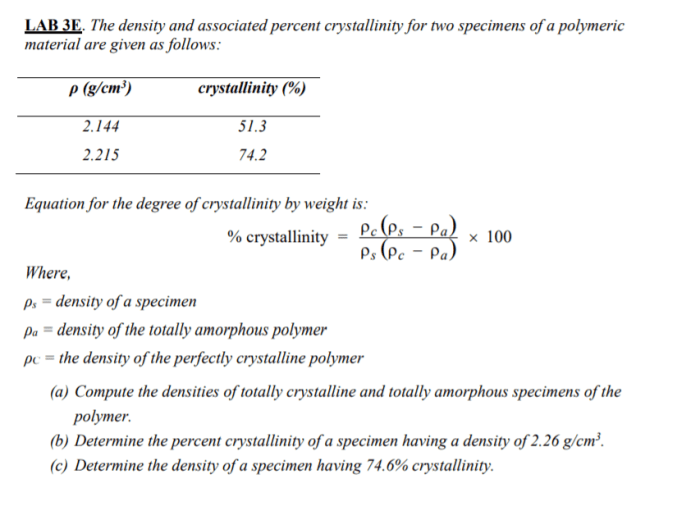
Relationship between Density and Percent Crystallinity, The density and associated percent crystallinity
| Material | Density (g/cm3) | Percent Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Crystalline Silicon | 2.33 | 100 |
| Amorphous Silicon | 2.20 | 0 |
| Steel | 7.85 | 90 |
| Glass | 2.5 | 0 |
The table above illustrates the relationship between density and percent crystallinity for different materials. Crystalline materials, such as silicon, exhibit higher density due to their ordered atomic structure. Amorphous materials, such as glass, have lower density due to their disordered structure.
Applications of Density and Percent Crystallinity Analysis
Density and percent crystallinity analysis find applications in various fields:
- Materials Science:Characterizing the properties of new materials, optimizing material processing, and understanding the relationship between structure and properties.
- Engineering:Designing and selecting materials for specific applications based on their density and percent crystallinity.
- Manufacturing:Controlling the properties of products through the manipulation of density and percent crystallinity.
Questions Often Asked: The Density And Associated Percent Crystallinity
What is the significance of density in materials science?
Density provides insights into the compactness of a material, revealing its atomic packing efficiency and molecular weight.
How does percent crystallinity impact material properties?
Percent crystallinity influences mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical reactivity, among other properties.
What factors influence the density of a material?
Atomic packing, molecular weight, and porosity are key factors that affect the density of a material.
What is the relationship between density and percent crystallinity?
Generally, higher density is associated with higher percent crystallinity, as crystalline structures are more densely packed than amorphous structures.