Embark on a journey of discovery with our comprehensive environmental science unit 1 test answers, meticulously crafted to empower you with a profound understanding of the fundamental concepts that shape our planet’s well-being.
This guide delves into the intricacies of ecosystems, unravels the significance of biodiversity, explores the pervasive impacts of pollution, and unravels the complex tapestry of climate change. Prepare to delve into the heart of environmental science, unlocking the knowledge that empowers you to make informed decisions for a sustainable future.
Environmental Science Unit 1 Test Answers

Unit 1 of an environmental science course introduces students to the fundamental concepts, definitions, and theories that underpin the field. These include the concept of sustainability, the interconnectedness of ecosystems, and the human impact on the environment.
Key definitions and theories covered in Unit 1 include:
- Ecosystem: A community of living organisms and their physical surroundings, interacting as a system.
- Biodiversity: The variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems.
- Sustainability: The ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- Environmental impact: The effect of human activities on the environment, both positive and negative.
Real-world applications of environmental science principles include:
- Pollution control: Developing and implementing strategies to reduce air, water, and land pollution.
- Conservation biology: Protecting and restoring threatened and endangered species and their habitats.
- Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the effects of climate change.
- Environmental education: Raising awareness about environmental issues and promoting responsible environmental behavior.
Ecosystems and Biodiversity

Ecosystems are classified into different types based on their physical and biological characteristics. Major types of ecosystems include:
- Terrestrial ecosystems: Land-based ecosystems, such as forests, grasslands, and deserts.
- Aquatic ecosystems: Water-based ecosystems, such as oceans, lakes, and rivers.
- Wetlands: Areas where water covers the soil for at least part of the year, such as marshes and swamps.
Biodiversity is essential for ecosystem health and provides numerous benefits to humans, including:
- Ecosystem services: Essential services provided by ecosystems, such as water purification, pollination, and carbon sequestration.
- Food and medicine: Biodiversity provides a source of food and medicine for humans.
- Economic value: Biodiversity supports industries such as tourism, agriculture, and biotechnology.
Threats to biodiversity include habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation. Conservation measures to protect biodiversity include:
- Protected areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and other protected areas.
- Habitat restoration: Restoring degraded habitats to support biodiversity.
- Sustainable practices: Promoting sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and other industries.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity and conservation.
Pollution and Environmental Health: Environmental Science Unit 1 Test Answers

Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances into the environment. Major types of pollution include:
- Air pollution: The release of harmful gases, particles, and aerosols into the atmosphere.
- Water pollution: The contamination of water bodies with harmful substances, such as chemicals, sewage, and agricultural runoff.
- Land pollution: The contamination of soil and groundwater with harmful substances, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial waste.
Pollution has significant effects on human health and the environment, including:
- Respiratory problems: Air pollution can cause respiratory problems such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
- Waterborne diseases: Water pollution can spread waterborne diseases such as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery.
- Ecosystem damage: Pollution can damage ecosystems and reduce biodiversity.
Strategies for reducing pollution and protecting environmental health include:
- Pollution control regulations: Implementing regulations to limit the release of pollutants into the environment.
- Clean energy technologies: Developing and using clean energy technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- Sustainable practices: Promoting sustainable practices in agriculture, industry, and transportation.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about the effects of pollution and promoting responsible environmental behavior.
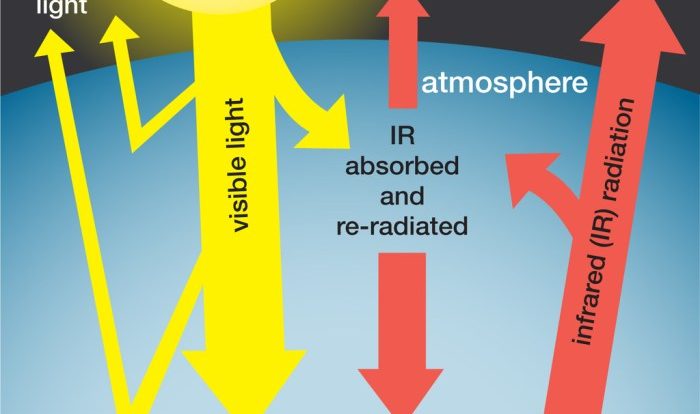
Climate Change and Sustainability

Climate change refers to the long-term changes in the Earth’s climate system, primarily driven by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Major causes of climate change include:
- Burning fossil fuels: The combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide.
- Agriculture: Agricultural practices, such as livestock production and rice cultivation, release methane and nitrous oxide into the atmosphere.
Consequences of climate change include:
- Rising sea levels: Climate change causes glaciers and ice caps to melt, leading to rising sea levels.
- Extreme weather events: Climate change increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heat waves.
- Ecosystem disruption: Climate change can disrupt ecosystems and reduce biodiversity.
Sustainable practices that can mitigate climate change and promote environmental sustainability include:
- Renewable energy: Switching to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sustainable agriculture: Adopting sustainable agricultural practices, such as agroforestry and organic farming, reduces greenhouse gas emissions and protects ecosystems.
- Forest conservation: Protecting and restoring forests helps to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Quick FAQs
What are the key concepts covered in Unit 1 of an environmental science course?
Unit 1 of an environmental science course typically introduces foundational concepts such as the scientific method, environmental systems, ecology, and the interconnections between human activities and the natural world.
Can you provide a summary of the important definitions and theories related to environmental science?
Environmental science encompasses a vast array of definitions and theories. Key terms include ecosystem, biodiversity, pollution, climate change, and sustainability. Theories explored may include population ecology, biogeochemical cycles, and the Gaia hypothesis.
What are some examples of real-world applications of environmental science principles?
Environmental science principles find practical applications in areas such as pollution control, conservation biology, environmental impact assessment, renewable energy development, and climate change mitigation strategies.